Studies show that consuming just 5-10 grams of soluble fiber daily can reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol by 5-10%, significantly boosting heart health.

High cholesterol is a silent threat that can harm your heart health.
With cardiac disease being one of the leading causes of death worldwide, understanding how to manage its levels is more crucial than ever.
While medication is an option, many people prefer natural, lifestyle-based solutions.
But have you ever wondered how people improve their heart health naturally by choosing different approaches?
This blog will help you learn different evidence-based dietary ways to reduce cholesterol and improve cardiovascular health.
From superfoods to smart swaps, you will see positive changes that can have a lasting impact on your well-being.
What is Cholesterol and why is it harmful?
It is a vital type of fat that circulates in the bloodstream. It plays a crucial role in building cells and producing hormones.
However, having more lipids, particularly the harmful variety, poses serious health risks.
Elevated levels can lead to plaque buildup in the arteries, which significantly increases your risk of diseases like stroke and other cardiovascular conditions.
Understanding how it works and taking decisive action to manage it effectively to maintain optimal heart health is imperative.
Opting for dietary ways is one of the most potent strategies for controlling it. Making deliberate and mindful food choices can significantly mitigate your risk of cardiovascular diseases.
This guide will outline how to implement different dietary and lifestyle changes for better and elevated well-being.
Cholesterol and its Type
Understanding its types is essential before opting for any solution to reduce its levels.
It moves through the bloodstream using two different lipoproteins that we will discuss in this section.
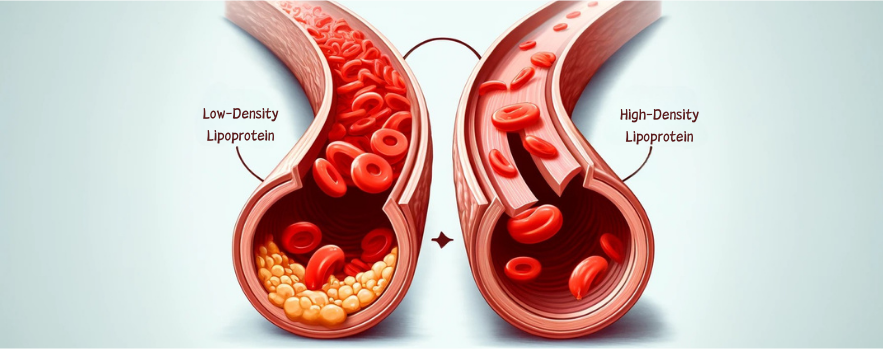
Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL)
It is often referred to as “bad” because it builds up in the walls of arteries, leading to significant plaque formation.
This plaque narrows and hardens the arteries, a condition known as atherosclerosis, dramatically increasing the risk of attacks and strokes.
High Density Lioprotein (HDL)
It is widely recognized as “good” because it removes excess amounts from the bloodstream by transporting it to the liver, which is effectively broken down and excreted.
Maintaining HDL is essential, as they are directly associated with a significantly lower risk of heart disease.
Both these types are essential for the human body but at a moderate level.
Since you have learned about the types, it’s time to learn about the factors affecting your cardiovascular health.
8 Dietary Ways to Reduce Cholesterol
Certain foods are proven to lower LDL and improve heart health. In this section, we will study some of these food items that you can use to keep your body fit:
1. Fiber-Rich Foods
- Soluble Fiber: Foods rich in soluble fiber can help lower LDL by binding it in the digestive system, preventing its absorption into the bloodstream. Adding soluble fibers, including oats, barley, beans, lentils, and fruits such as apples and pears, helps reduce LDL.
- Benefits of Fiber: Soluble fiber lowers total lipids, reduces blood pressure, and promotes overall heart performance.
2. Healthy Fats
- Unsaturated Fats: Substituting saturated ones with unsaturated food items to reduce LDL while increasing HDL levels. It can be found in olive oil, avocados, nuts, and seeds, another dietary way to lower cholesterol.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: They are found in fatty fish such as salmon and mackerel, flaxseeds, and walnuts, which are highly effective at reducing LDL levels and inflammation. Additionally, they actively increase HDL, solidifying their status as a vital choice.
3. Plant Sterols and Stanols
- Found in Fortified Foods: They are natural compounds in plants that help reduce fat absorption in the intestines. They are commonly added to margarine, orange juice, and yogurt.
- Mechanism: They can help lower the absorption of unhealthy fats in the body.
4. Soy Protein
- Sources: Soy proteins can help reduce LDL absorption in your body. You can also fulfill your daily protein intake.
- Role in Cholesterol Reduction: Research indicates that regular consumption of soy protein can lower LDL levels, making it a beneficial part of your diet.
5. Foods to Avoid to Maintain Healthy Lifestyle
Many foods effectively lower LDL levels, but some can raise it. Avoiding these food items in your lifestyle and diet to reduce cholesterol levels will help you maintain your fitness.
Saturated Fats
- Sources: These are mainly found in red meat, butter, cheese, and processed meats.
- Effects: It elevates LDL, directly contributing to plaque buildup in the arteries. Reducing their intake is crucial to manage the lipids effectively.
Trans Fats
- Sources: They are prevalent in hydrogenated oils, baked goods, and snacks like chips and cookies, making them a significant component of many processed foods.
- Harmful Effects: They pose a serious threat to heart health. They significantly raise LDL levels and lower HDL, making them some of the most dangerous dietary components you can consume.
Excessive Sugar and Refined Carbohydrates
- Sources: Sugary drinks, baked goods, and white bread contain refined carbohydrates and sugars. Avoiding these items helps to reduce bad cholesterol and live a better lifestyle.
- Connection: Excessive consumption of sugar and refined carbohydrates directly increases triglyceride levels, which significantly increasing the risk of heart disease.
6. Increase Consumption of Antioxidants
- Fruits and Vegetables: Berries, spinach, kale, and other vibrant fruits and vegetables are packed with antioxidants that reduce inflammation. Incorporating these foods into your diet is essential for maintaining optimal wellness.
- Benefits: Dietary foods high in antioxidants protect arteries from damage. Adding these food items to your daily eating habits will lower the risk of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases.
7. Moderate Alcohol Consumption
- Excessive Alcohol: Consuming excessive amounts of alcohol can raise blood pressure and lead to higher cholesterol.
- Potential Benefits of Moderate Wine Intake: Moderate consumption of wine, especially red wine, has been shown to increase HDL and provide heart protection. However, moderation is essential to limit intake to one drink per day for women and two for men.
8. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
- Link Between Weight Loss and Cholesterol: Reducing excess weight can significantly lower LDL and enhance overall cardiac health.
- Dietary Strategies: To manage weight, prioritize different ways to control portions, and engage in regular physical activity.
These are some of the dietary practices that you can accumulate in your daily routine to improve your overall heart by reducing cholesterol levels.
Lifestyle Tips to Support Dietary Changes

To reduce lipid levels and support healthy living, you can accumulate diet tips to reduce cholesterol and achieve your goals.
Here are some guidelines that you can follow in your dietary ways to reduce cholesterol and make your lifestyle better:
1. Physical Activity
- Aerobic activities such as brisk walking, running, cycling, or swimming for at least 150 minutes a week can significantly improve blood levels.
- Strength training, including weightlifting or resistance exercises, twice a week helps reduce LDL and increase metabolism, which is essential for heart health.
2. Stress Management
- Practicing mindfulness or meditation for 10–15 minutes daily reduces stress and improves mental health.
- Activities like yoga, deep breathing exercises, or progressive muscle relaxation are excellent for stress management.
- Engaging in hobbies such as gardening, reading, or painting can provide emotional relief and reduce stress.
3. Meal Planning
- Planning meals can help you to reduce LDL, including soluble fiber, nutritious fats, lean protein, and plenty of vegetables.
- Performing beneficial snacking, such as nuts, fruits, or whole-grain crackers, to curb hunger and avoid processed foods.
- Batch cooking helps you to prepare large portions of meals, like soups or stews, and store them for the week to save time and ensure consistency.
Common Myths about Cholesterol and Diet
Managing these things simultaneously can be confusing, especially given the widespread myths about dietary methods and fats. Misconceptions often lead to unnecessary food restrictions or unhealthy choices.
Let’s unravel some common myths about their connection, helping you make informed decisions about dietary ways to reduce cholesterol levels, leading to a healthy heart.
Myth 1: All fats are harmful
Fact: Not all triacylglycerols are bad for your body. Nourishing ones, such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated, are crucial for maintaining HDL levels and overall fitness.
- Healthy Triacylglycerols: Found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, they help reduce LDL and increase HDL, which improves heart health.
- Harmful Triacylglycerols: Trans and excessive saturated fats are the real culprits in raising LDL levels. Avoid these by reducing your intake of processed and fried foods.
Takeaway: Focus on incorporating heart-healthy triacylglycerols into your dietary foods while minimizing the harmful ones for better management.
Myth 2: Eggs always raise cholesterol
Fact: Eggs have been unfairly demonized for their fat content. While they contain dietary lipids, research shows they do not significantly impact blood fat levels in most people.
- How It Works: For many individuals, the liver adjusts the lipid production when good lipids intake increases, minimizing the effect.
- Who Should Be Cautious: People with certain conditions, like familial hypercholesterolemia or type 2 diabetes, should monitor their egg consumption and consult a healthcare professional.
Takeaway: For most people, eggs can be a rich source of protein and nutrients.
Myth 3: Cholesterol-lowering foods work instantly
Fact: Oats, nuts, and fatty fish are highly effective foods that help reduce LDL. However, their benefits take time to manifest. As these foods become a regular diet, resulting in decrease gradually.
- Why It Takes Time: It is absorbed and metabolized over weeks, not days. For long-term improvement, consistent dietary changes and a heart-healthy lifestyle are required.
- Patience is Key: Combine these foods with other strategies, such as regular exercise and avoiding trans fats, to see sustainable results.
Takeaway: There is no quick fix for high lipids. To achieve lasting results, maintaining a good lifestyle will aid you in reducing cholesterol levels.
Conclusion
Opting for a diet that manages cholesterol will help prevent heart disease and ensure a long, healthy life.
You must incorporate dietary ways to reduce cholesterol levels, such as fiber-rich foods, plant sterols, and soy protein, while eliminating saturated and trans fats.
This approach will effectively lower your LDL cholesterol and enhance your cardiovascular health.
Furthermore, you should prioritize increasing your intake of antioxidant-rich foods, moderating your alcohol consumption, and maintaining an appropriate weight.
Remember, effective cholesterol management requires more than just dietary changes.
To achieve optimal results, combine a heart-healthy diet with regular exercise, stress management, and other good lifestyle habits.
Start making small, sustainable changes today to secure a healthier tomorrow.








